Opinion dynamics 1: Social contagion moves hearts and minds
How to win elections and influence people
August 29, 2020 — March 3, 2022
Suspiciously similar content
Assumed audience:
Campaigners without background in modern viral marketing
Content warning:
This entire post is about communication in a hostile environment between people of different opinions on controversial topics and links to examples of those opinions, which are, in context, potentially offensive to people of opposed opinions
A campaigner friend asked this question:
What’s the least dense, most accessible article to introduce people to the idea that opinions are an emergent property of social networks?
What a great question. I do not know a good introduction to social contagion theory of opinions… So I’ll draft one real quick.
This post covers the following main points:
- We should start by assuming that social contagion is the main way we humans get our political opinions.
- We should lean into point #1 because we humans are wired to underestimate the importance of #1.
- We should lean into point #1 because other things that look like they are important often end up being about point #1.
- We should really lean into #1 because even if it were to turn out that points 1, 2 and 3 were all nonsense, social contagion would still be where campaigners can achieve leverage most cheaply.
Too many points? We can summarize the summary thusly:
tl;dr If you want a good strategy to move hearts and minds, start by treating people’s beliefs as contagions transmitted through their social network.
This idea is what we call “obvious (once you know the answer)”, in that once you start thinking this way it seems obvious. But it is not, for most people, obvious before you start thinking that way. Certainly, it did not always seem obvious for me. I think that this is common, that most people who have experience with social contagion of ideas forget that not everyone thinks in these terms, and thus we do not spend time making the case that this is a good way of thinking about things to laypeople.1 And that might be why I cannot find a good introduction to this topic; no one who knows it seems to feel it needs mentioning.
Anyway! Without further ado…
1 Background: The science of disease before contagion
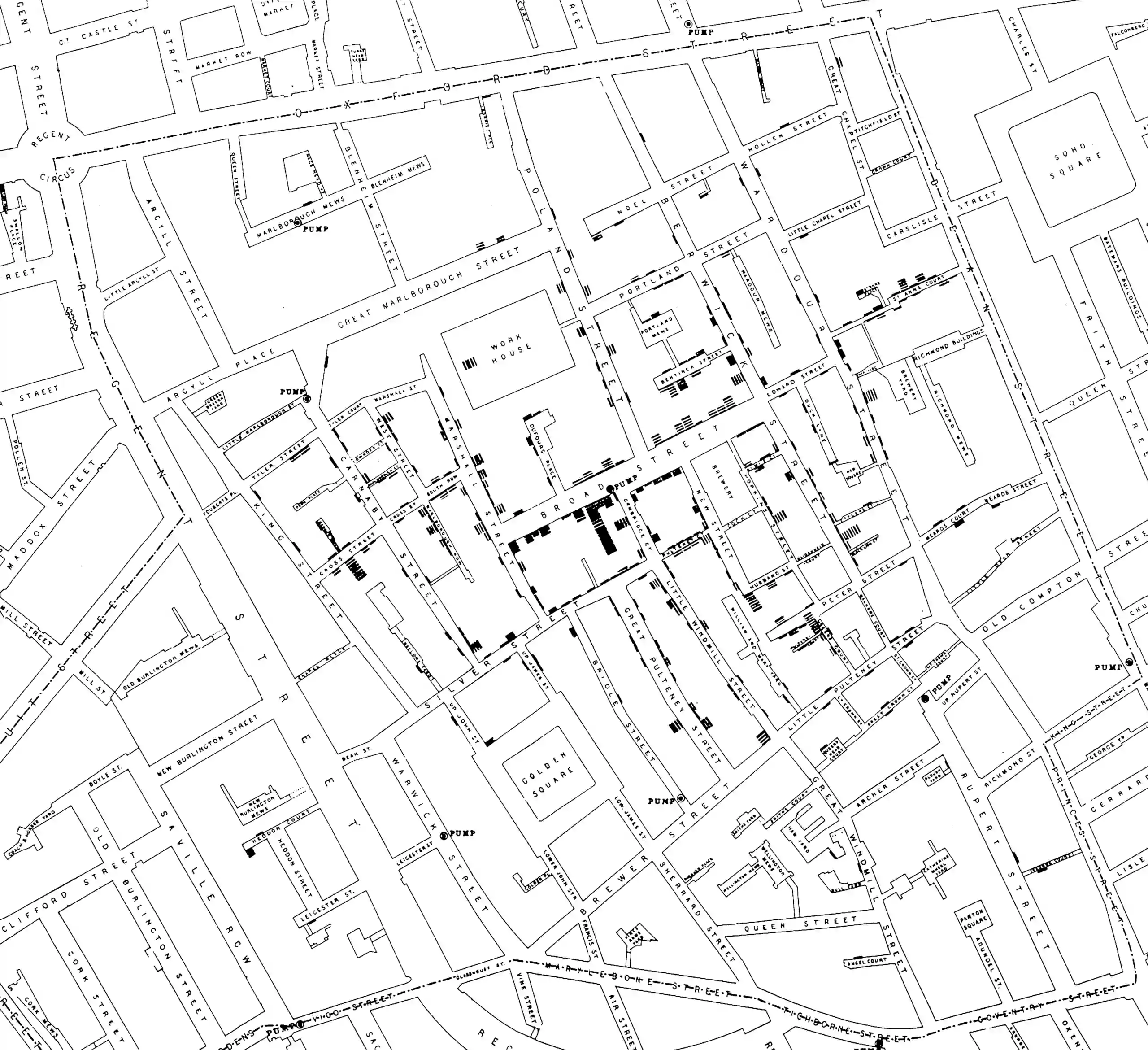
You might recognise this famous map, which marked a turning point in our understanding of contagious diseases.
This map was made by London physician John Snow, of the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak. Before his slam-dunk demonstration of the importance of germ theory, prevailing opinion was that cholera was induced by “miasma”, some kind of noxious gas associated with corpses. These corpsey miasmas were supposed to transmit cholera to people. And indeed, cholera was associated with corpses but not quite in the way they supposed. If you are around the stinking unsanitary conditions that cholera epidemics frequently arose in, of course you might feel that you are at dangerous risk of disease. But there is a massive difference between how you can make yourself safe from germs that arise from people, and noxious miasmas that come from the ground. Until Snow’s decisive evidence of this new-fangled person-to-person germ theory, we did not have the tools we needed to manage this disease; authorities could not untangle correlation between cholera cases from the common underlying cause of those cases.
With the understanding that cholera was transmitted by the bacteria, which came ultimately from other people, came the power to be vastly more effective in cutting off disease. In particular, in identifying that affected people around Broad Street were all getting their water from a single pump, which ended up being contaminated by a sick baby, they could cut off the water supply at that pump.2
Of course, this was not to say that there was nothing more to learn about cholera. They had yet to identify the relevant bacterium, invent antibiotics and so on. But until they understood that the cause of disease was something transmitted between people rather than something oozing out of a place, they could not even ask the right questions to understand that disease better. Scientists could spend all day shoving flowers up their noses to identify the one that seems to do the best at “stopping miasmas” but they will do a terrible job at identifying what is really going on. On the other hand, once they know about the transmissibility of the disease they can ask all sorts of useful questions: Is keeping food and drink free from contamination helpful? Is it airborne? Which bacterium is responsible? Does heating kill it? Soap? And so on.
For some reason, difficulty in understanding contagion is a recurring feature of human history. Time and again we have been reluctant to see diseases as contagions we catch from other people, preferring to imagine they are caused by something in the environment. Consider Ignaz Semmelweis’s battle to introduce hand-washing amongst doctors, or the arguments on Twitter that 5G towers cause COVID-19 and so on.
And of course some illnesses (say, scurvy3, or leukaemia) are indeed caused by the environmental factors.4 So it’s not crazy to ask whether something is contagious or not, or even whether contagiousness is only one of several factors contributing to a disease. What does not make sense is to assume it is not contagious.
In many organisations and industries, we are in a “pre-germ theory” stage when it comes to understanding opinions. Often, we restrict our analyses of human behaviour implicitly to “miasma”-type theories, never leveraging the modern understanding of how ideas are themselves contagious things, transmitted person-to-person. And yet, the data is there to suggest that opinions are very contagious indeed. We have an embarrassment of data that suggests that opinions people hold are strongly determined by the opinions and behaviours of their friends, and transmitted through interpersonal relationships. So, we have reason to be sceptical of theories of belief which omit social contagion.
To pick an extreme example, people will copy the behaviour of their friends even unto death: 134 people burned to death in the notorious Beverly Hills Supper Club fire after failing to evacuate until much too late even when someone repeatedly raised the alarm.5 Now, did those people fail to evacuate because they had an innate preference for burning to death? Did a miasma of fire ignorance repress their better instincts? Was there no feasible way they could fact-check the existence of a fire?
A better explanation for this tragedy seems to be that, as far as the patrons were concerned, an epidemiological explanation for the belief. Their friends at the same table were not behaving as if that fire was real or important, and so why should they be the first to step out of line? There are many lessons there, but crucially for the current purposes it is that even at the risk of their lives people would prefer to act and think like their neighbours than fact-check their neighbours.
It might be tempting to imagine this example is abnormal but this kind of thing is famously easy to reproduce in the lab. This is well studied in the form of the bystander effect (Darley and Latane 1968; Latane and Darley 1969). And we all know many examples from history of collective delusions, false beliefs, millenarian cults, panics and other madnesses of crowds. The thing is, we are often reluctant to imagine that this madness-of-crowds dynamic might be ubiquitous in human life. Even if we do accept that idea though, that crowds are crazy, that beliefs are infections, we usually imagine it is that crowd of those people over there. Specifically, we, you and I, typically resist imagining crowd madness in ourselves, personally, right now. “Having a reasoned opinion,” however, is also what catching a contagious opinion feels like from the inside.
Being in thrall to ideas that we thoughtlessly catch from people around us is not necessarily a bad thing. Just because we caught a belief from a friend does not mean it is false. The belief that aeroplanes can fly would have seemed like collective madness a couple of centuries ago. These days, that belief is normal, and it is probably just as well for the efficiency of the airline industry that each passenger does not stop during the boarding process to check the equations of the Boeing engineers for themselves. On the other hand, just because a belief is contagious does not mean it reflects the truth of the world. And just because it feels true does not mean we did not thoughtlessly acquire it from our friends or family.
Both true and untrue beliefs have a deeply social element. Perhaps because our antennae are so tuned to receive contagious beliefs and adopt them as our own, we find it easy to overlook that element in ourselves and in others. Whatever the basis, we can observe it is hard to think about beliefs as contagious. If we want to influence what people out there in the world believe, then we need to make that social element explicit, and work with it, or we are doomed to misunderstand the dynamics of influencing people, and do it badly.
And in fact, in many industries and fields, it is common to analyse beliefs with the same tools we use to analyse contagious diseases. In viral marketing, in internet modelling, in economics and in political science, we create and use epidemiological models of the spread of beliefs all the time. So, let us examine what these kinds of models are exactly, and how they differ from non-network models.
Very good. So I have argued that we need to consider contagion-explanations when understanding beliefs, and that we should not expect that those explanations should be instinctually obvious. What next?
2 It’s not what you know it’s who you know
Having argued that it is important to consider the contagiousness of beliefs, we need to get more specific so that we can make stronger statements. I do not want to try to come up with a complete epidemiological theory of why anyone believes any kind of thing ever, and the details of which beliefs have which degree of contagion and so on. Here, we are specialising our model, considering political opinions in particular.
- Political opinions
- Political opinions and beliefs_ are opinions and beliefs about how our society does work and how it should work, at a large scale.
There are two things that are special about this class of opinions:
- mustering political opinions in your support is essential, at least in a democracy, for getting things done
- political opinions are likely to be especially socially contagious for reasons that I will expand on in a moment.
What is special about “political” opinions/beliefs is that most of them are formed far from evidence. Political opinions are ones where we, as private individual citizens, will not get to see all the evidence first hand, because there is just too much of it. “Fire is hot” is not a political opinion, because I have all the evidence I need to support that and scars to prove it. “We need to put more funding into preparing to fight bushfires”6 is a political opinion. “Bushfires are made worse by climate change” is a political opinion. “Covid vaccines are more (or less) dangerous than COVID-19” is a political opinion. And yes, “I should vote for [your choice of] party” is a political opinion.
All these opinions might in actuality correspond to true facts about the world (or not) but whether we hold those opinions is only remotely connected to whether those opinions are true.
You will notice that I am using belief and opinion as synonyms here, which might feel uncomfortable. In my opinion, there is no useful difference between belief and opinion, at least not in our current purposes.
Most of us are not bushfire survivors, but if our society has to develop a shared policy to deal with bushfires then we might all be asked to have an opinion on bushfires. These issues, where we all have an opinion but few of us have much information, are the ones where we expect the behaviour to be especially contagion-like. These are the circumstances in which contagion-type behaviour becomes important. We are less likely to see a huge outbreak of fire-denialism, than we are to an outbreak of climate-change denialism. When the connection to personal experience is remote, the dominant factor driving our belief is presumably social, which is to say, something best understood as a transmissible thing like a disease.
In contagious beliefs like this we usually consider the social network as a unit of analysis.
- Social network
- Social network is now the language we use to discuss online social media apps like TikTok or Facebook or Instagram. I am using social networks in a broader, older sense here. Sure, it might include Facebook connections or whatever, but really I mean any repeated, interpersonal connection. If you talk to the barista at your local coffee shop, that barista is in your social network. Your co-workers are in a social network with you.
In social network models we start from the perspective of the social relationships between people if we want to understand why they do a thing. If we want to understand why someone has a belief, we look at who might have transmitted it to them.
We can also imagine other factors, miasmas if you like, which might influence their belief, but a priori we suspect these factors are usually secondary influences upon political beliefs. No one is born with an innate opinion on the dictatorship of the proletariat or an appropriate maintenance schedule for the local government’s public gardens.
Because this is political science now, not epidemiology, we don’t talk about miasmas but refer to these as factors, or features. A sampling of such factors might be e.g. people are homophobic because of a particular brain structure (e.g. Ahn et al. 2014) or pro-environmental because of their genes (e.g. Chang et al. 2021), authoritarian because of economic stress (e.g. Ballard-Rosa et al. 2021), or conservative because of intrinsic values (which are presumably fixed in childhood) (e.g. Sheldon and Nichols 2009)… These various factor theories all suggest different dynamics that we expect to observe in popular opinion, and different ways we might influence popular opinion compared to network-type theories. In these factor theories, we lump people together based on factors such as race, age, gender, what-have-you, and try to analyse what people who possess similar factors are like.
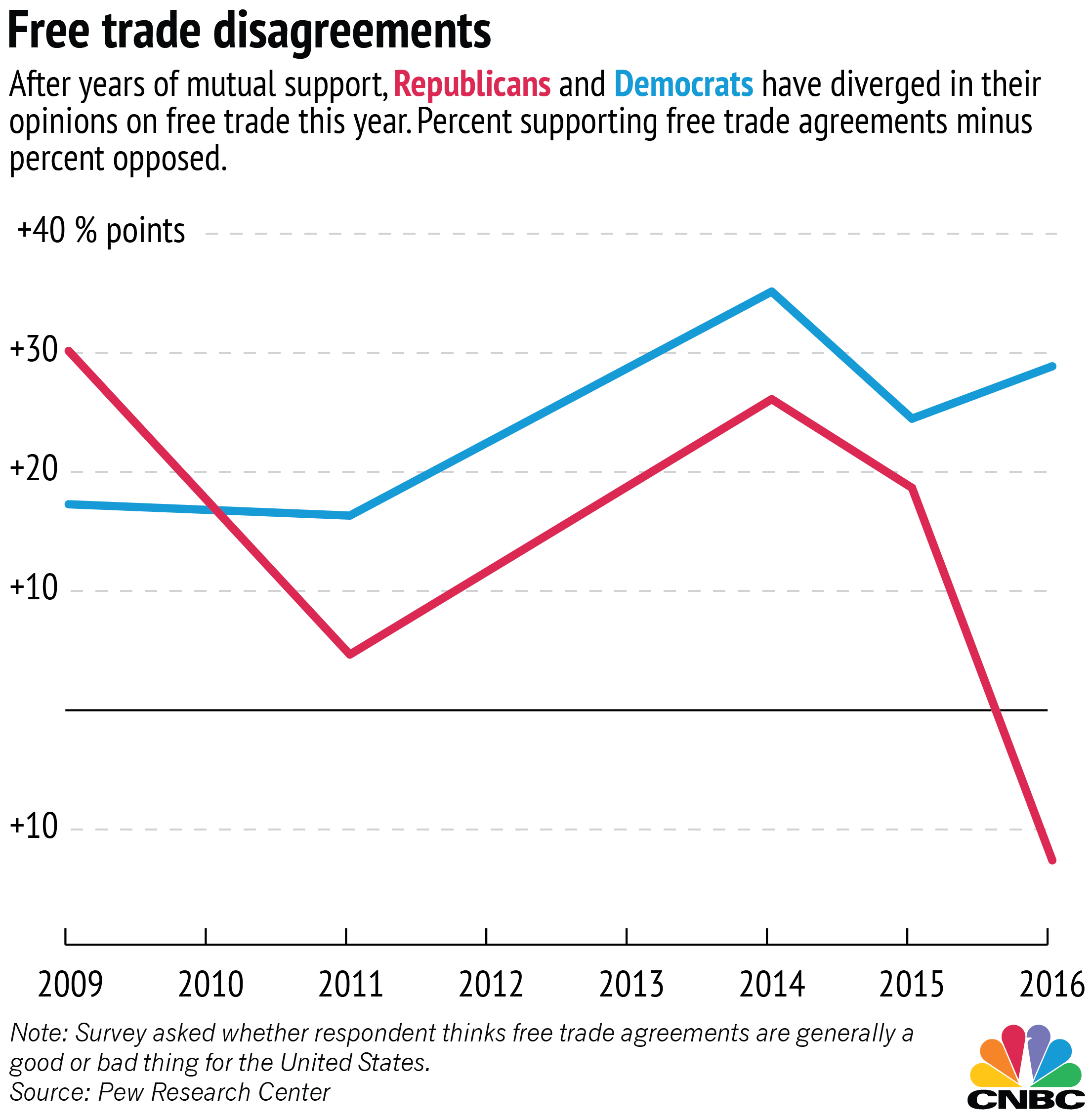
So why should we favour network models? One reason: because contagion-type behaviour is important in describing the massive shifts in politics that we observe in the world around us, right now. One piece, (via Tanner Greer) shows a particular opinion about free trade ripping through voters like COVID-19 through an unvaccinated population:
It is hard to find an explanation for this kind of behaviour in terms of miasmas. The genes, brain structures and economic circumstances, fundamental values etc of American Republicans did not change drastically from 2015 to 2016 but their support for particular policies did. What is going on? Well, that one, I assert, might well correspond to the rise of Trumpism, with Donald Trump as patient zero in that outbreak.7 People are attending rallies, talking to their friends and otherwise doing all the business of meeting people and taking on new opinions.
For another example, we could consider the deep canvassing model, devised by the Los Angeles Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Center in California.8 The research is great at showing how to talk to people to change their minds, but also, crucially, it demonstrates the effectiveness of changing minds by person-to-person contact.
Contagion-type, network-based models can easily support the kind of dynamical changes like this contagion, whereas the implicitly static models cannot. Just as we remained COVID-free for a very long time, then some of us who came into contact with COVID-patients acquired COVID, so can a public opinion remain dominant for a very long time then be overturned rapidly by a well-connected spreader. This also brings us to another important insight about social contagion: It suggests that we can, sometimes, produce massive changes in opinions, even apparently deeply held ones, by influencing people through their peers.
There are other models, of course. We might imagine a high-budget advertising campaign changed opinions in this case. And indeed, advertising probably plays a role here too. But advertising is at the best of times an uncertain way of producing change, and we are generally suspicious that it can do anything like exponential spread through a population. Moreover, it is not incompatible — might advertising accelerate social network changes rather than cause it? How do we know, without investigating both these in concert?
4 How about this contagion idea in particular?
In modern social research we now have much terminology to categorise and understand the crucial social component of human behaviour. One technical distinction that is useful for the current purpose to us is homophily versus contagion. When we observe a group of people and we wonder why they exhibit a certain behaviour we might explain that in terms of causes.
- Homophily
- This group of people behaves in such-and-such a way because similar people will form a group together
- Contagion
- This group of people behaves in such-and-such a way because people who are in the same group tend to know each other.
Do political parties form policies that suit their members’ innate preferences (homophily)? Or do political parties exist and persuade their members to prefer certain policies (contagion)?
If your goal is to get certain policies accepted then the difference between these two ideas is very important.
Social network theories are ones that start from the premise that we want to study people in the context of the factors they possess, or their connections within their social network. For the sake of exposition, we might characterise theories into “factor” and “network” type theories.
How exactly this happens is a massive research area. A lot of academics and industrial researchers have spent a lot of time and money trying to pin down the details of how belief is socially transmitted.
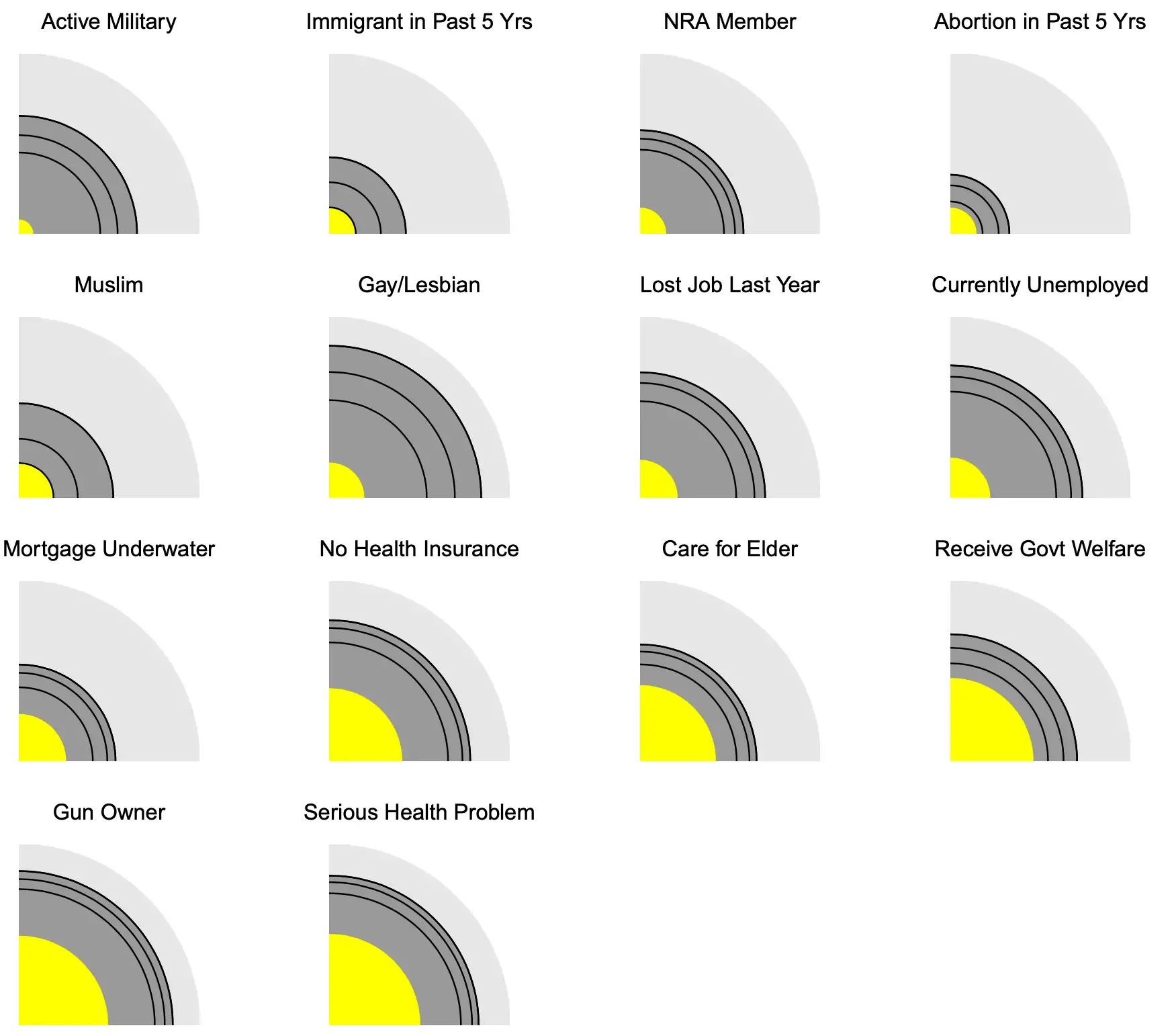
One ripper example of how to do this is the social penumbra paper (Gelman and Margalit 2021).9 This paper examines one particular quality of social graphs: how engaged the members of a certain group are with people outside that group.
Our study makes three contributions. First, it introduces the concept of penumbra as a relevant political characteristic of social groups, shifting the focus from the groups’ members to features of the group’s social circle (i.e., its outward contacts with nongroup members). Second, we provide a set of estimates of the penumbras of an array of different groups in society and highlight the significant variation in the penumbras’ size and characteristics (e.g., in terms of income, education, political leanings). Finally, we provide preliminary evidence regarding the political significance of penumbras, demonstrating that a change in penumbra status is in some cases also associated with shifting views on policy matters related to the group in question.
So, this is about groups that have learned to adopt a certain strategy of visibility and engagement with the society around them, and thereby succeeded in shifting social support for policies of interest to that group.
For example, about 3% of the US population identifies as gay or lesbian, about half the share of people with a mortgage “under water” at the time of our survey. Yet, the sizes of penumbras of the two groups go in the opposite direction, with 74% of respondents saying they knew at least one gay person and only 35% reporting that they knew someone whose mortgage is under water.… if a group such as underwater mortgage holders is hidden to much of the general population, this will affect the extent to which their problem becomes salient and how it is perceived by the public. These differences thus suggest why specific policies such as same-sex marriage and debt forgiveness to mortgage owners, while directly affecting similarly sized groups, could resonate very differently across the broader population.
This paper suggests that a group’s success in changing the beliefs and policies of broader society is strongly influenced by their success in making themselves both visible and engaged beyond their own group. This is true whether you’re talking about gun owners who’d like unrestricted access to semi-automatic assault weapons, or LGTBQI+ people who’d like to get on with their private lives without discrimination. In short, repping matters - take the pride out of gay pride & it might be a less powerful campaign. Pride is intrinsically a network phenomenon, about acceptance within your network and amongst your peers, and learning how to propagate that acceptance to the mainstream has led to massive strides in legal support for this community.
There is much more material examining the social network structure of contagions; We see it in everything from exercise habits (Aral and Nicolaides 2017) to alt-right mobilising (Ribeiro et al. 2019). For a link dump on that theme, see memetics. For now, let us take it for granted that a lot of people think this is an important concept, and look at it from a different angle.
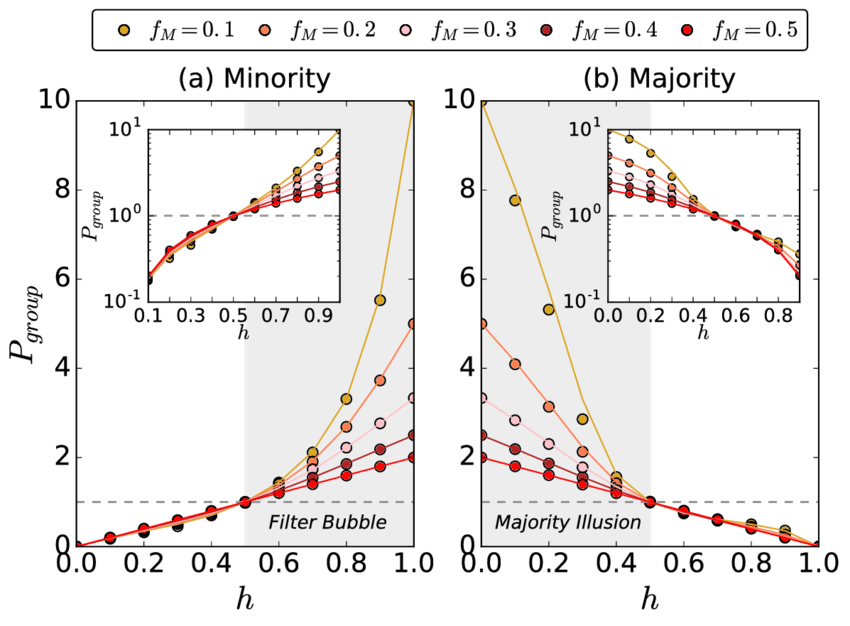
8 Majority illusions and visibility
TODO: explain how huge this possibly is.
In homophilic networks (0.5 ≤ h ≤ 1), the minority overestimates their own size (filter bubble) and the majority underestimates the size of the minority. The insets show the same information on log scale to make the amount of underestimation and overestimation comparable. As group sizes become more disproportionate, perception bias increases. (Lerman, Yan, and Wu 2016)
9 Conclusion
10 Postscript: Did this help you?
NB: I am curious about the number of people who will gain something from this post. On one hand, hipster, up-to-the-minute viral marketers in tech startups will be aware of the outline of much content here, as it is their bread and butter and they have data to back it. On the other hand, you can get at many of the same conclusions by classic, intuitionistic old-school social organising, of the kind that is centuries or millennia old, and they have history to back that. In between these vintages, there seems to be a cohort of people who seem to make do with curiously little social network theory. This is my target: Social campaigning’s middle children (Hello if this describes you, middle child!) You might fit into this category if you acquired your ideas of human behaviour by osmosis from the google analytics dashboard, or maybe if you have never tried to measure your effectiveness in the world at all. Regardless, whoever you are, I would welcome feedback.
11 TODO
- Damn it, Ignaz Semmelweis and Joseph Lister would have been better examples than John Snow.
- follow-up about how to use social graphs in practice. Are all social relationships equal? In fact, that will be in opinion dynamics II
- Mention that this miasma/network setup is over-simplified, but it is a passable intuition pump-prim as we move to more advanced stuff
12 References
Footnotes
If you work in social media research or in viral marketing, or weaponised social media engagement, or troll farms, at this point you might be way past wondering why I am bothering explaining that your job is real. This essay is not for you! Maybe some writing on virality or the theory of social graphs.↩︎
For more on this story see Simon Rogers, John Snow’s data journalism: the cholera map that changed the world↩︎
Interestingly, Scurvy was erroneously believed to be caused by germs for a while↩︎
Genes are of course also a factor for many diseases, and in turn interact with the other factors in complicated ways, but that is a story for another textbook.↩︎
The story of that fire is super interesting, by the way. Go and listen to Tim Harford’s podcast about that fire, if you’ve not heard about it.↩︎
wildfires for Americans↩︎
We might also imagine that political opinion happens through some other process, such as reasoned debate, or through media persuasion. We’ll come back to those options later.↩︎
There is a fascinating scientific scandal in the history of this idea, what with the famous LaCour study, which was fake, and the Broockman and Kalla study (Broockman and Kalla 2016), which was real. There is a convenient Dave McRaney podcast on this theme.↩︎
The experiment design in this paper, by the way, is extremely clever. Experiment design is not really our focus here, but another thing a campaigner could also learn from this paper is how to design surveys to indirectly extract high reliability information from average punters. Do your surveys identify the size of someone’s social circle by asking them how many Marias they know?↩︎
I think of this as the Dunning-Kruger theory of mind.↩︎







6 Social contagion sets us up to ask useful questions about how we can make a difference
Meanwhile in Australia, Jakubowicz and Ho, in Was there an ‘ethnic vote’ in the 2019 election and did it make a difference?, correlate conservative policy preferences to ethnic community prevalence. There is not necessarily anything wrong with that per se. But consider the types of interventions that are suggested by considering this as a factor rather than a network problem. In the network version, a person’s Chinese ethnicity is an indicator that they are likely to have a social network including an above-average number of other ethnically Chinese people. If the people in this individual’s network were disproportionately likely not to vote for my preferred candidate, then I am encouraged in a social network model to imagine ways in which I bring this individual and my candidate’s social networks together to change this preference.
On the other hand, if I imagine Chineseness is an immutable fact leading to intransigent opposition to my preferred candidate then I am left with little to do to further my candidate’s interest. At least, little that I can do in a modern social democracy, where disenfranchising or expelling ethnic groups or other categories based on the presumed political alignment is something we leave to authoritarian states.
Static factor models invite us to consider people as obstacles. Immutable factor models, that is, tend to suggest despair or despotism. Network models invite us to consider other human beings as precisely that. Social network models, that is, tend to suggest democratic engagement.