Soft incentive mechanism design
Markets, cakes, karma, and reverse game theory, applied to humans
September 22, 2014 — July 9, 2024
Suspiciously similar content
Mechanism design for the imperfect moral wetware of human beings. In practice, that means we might relax some of the mathematical axiomatization and consider more qualitative/fuzzy ways of thinking about it that are more “inspired by” formal algorithmic/game-theoretic models than presuming exactness. What do our rarefied abstract models of mechanisms imply for societies at large?
“Reverse” game theory, bargaining, auctions, pie slicing, swarm sensing for autonomous agents. Reputation mechanisms. Voting systems are mechanisms. The classic controversial one, assassination markets, are no longer at the vanguard. Prediction markets are a classic incentive mechanism for distributing forecasts (Merchant 2020). Every blockchain-style cryptowhatsit is a mechanism design problem. More important for this notebook, better governance can benefit from mechanism design.
One might frame adversarial learning as mechanism design.
It is worth knowing the concepts of mechanism design. It seems like the alternative to explicit mechanism design is bad implicit mechanism design.
1 Performance targets
Harder than we imagine. See Goodhart’s law.
2 Iterative conversation games
See iterated conversation games.
3 Voting systems
Democracy is the soft mechanism built upon the hard mechanism of, among other things, voting systems.
4 Selling a mechanism to laypeople
Sometimes, I notice that for many people thinking about how we might design incentive systems seems to be taboo. I suspect that this is because making things morally wrong is part of how human brains internalize collective action problems.
Observationally, I can get more buy-in to a conversation about mechanism talking about “fair systems” without talking about “incentives”, I think because if we talk about incentives it sounds like we might be bribing people, or encouraging greed. Sometimes we surely are doing that. I find this latter type of fuzziness uncomfortably disingenuous, but if the outcome is the same, maybe it’s OK.
5 Examples
- Choron is a case study in designing a mechanism for handling house chores.
6 Incoming
Hamilton Nolan, Everyone Into The Grinder
An interesting statement of a mechanism design problem.
One of the most direct ways to improve a flawed system is simply to end the ability of rich and powerful people to exclude themselves from it. If, for example, you outlawed private schools, the public schools would get better. They would get better not because every child deserves to have a quality education, but rather because it would be the only way for rich and powerful people to ensure that their children were going to good schools The theory of “a rising tide lifts all boats” does not work when you allow the people with the most influence to buy their way out of the water. It would be nice if we fixed broken systems simply because they are broken. In practice, governments are generally happy to ignore broken things if they do not affect people with enough power to make the government listen. So the more people that we push into public systems, the better.
I would like to make the thesis there a little more precise, but there is something there.
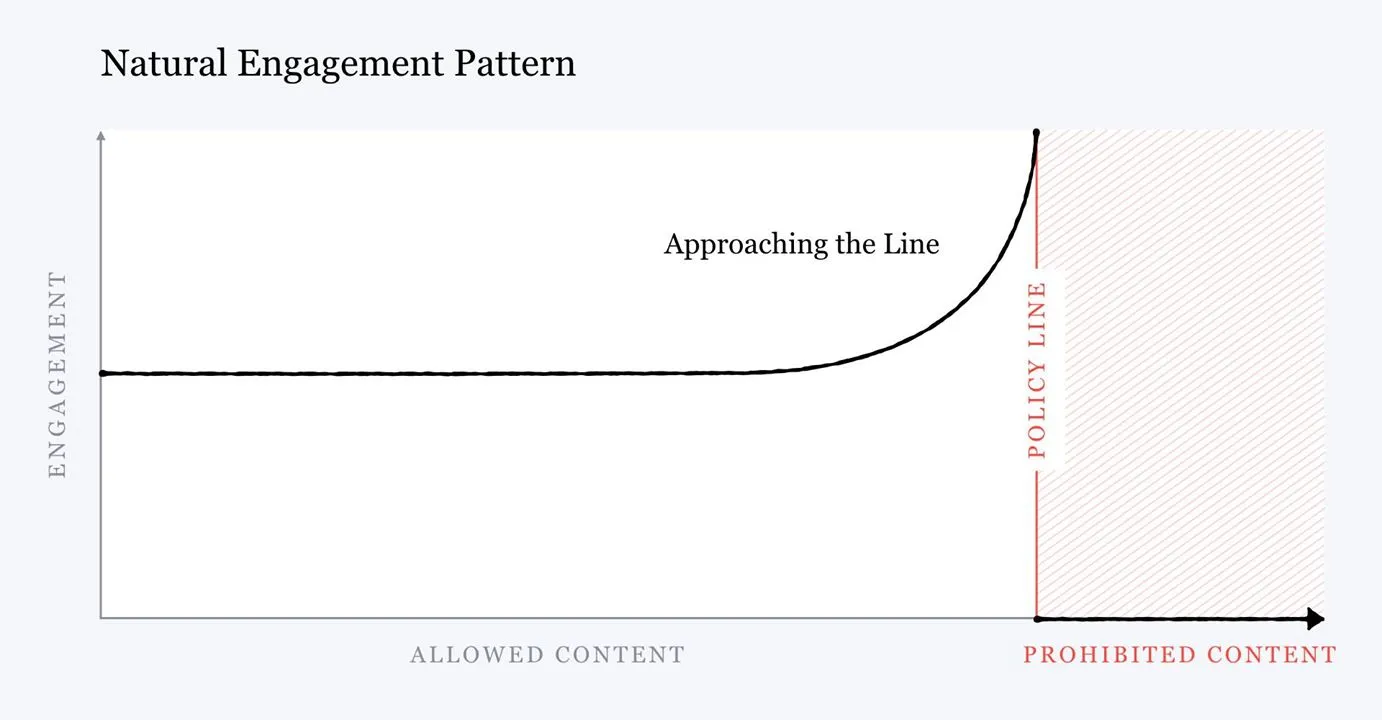
Facebook will change algorithm to demote “borderline content” that almost violates policies
Dàzéxiāng Qǐyì is the name of the perverse incentive uprising during the Qin dynasty
Chen Sheng and Wu Guang were both army officers who were ordered to lead their bands of commoner soldiers north to participate in the defence of Yuyang (simplified Chinese: 渔阳; traditional Chinese: 漁陽). However, they were stopped halfway in present-day Anhui province by flooding from a severe rainstorm. The harsh Qin laws mandated execution for those who showed up late for government jobs, regardless of the nature of the delay. Figuring that they would rather fight than accept execution, Chen and Wu organised a band of 900 villagers to rebel against the government.
Measurement and power in organisations (which mentions the Hubbard book on measurement) (Hubbard 2014). Great book, by the way; see analytics