Akrasia
Description to come later
June 18, 2017 — September 9, 2023
A useful insight from behavioural economics is that coordinating between my past self, my current self, my near future self, and my far future self is a difficult cooperation game. I sometimes think of time management as a mechanism design problem where all the players are me, at different points in the past and future.
Akrasia is the beeminder term for thinking about this.
Akrasia (ancient Greek ἀκρασία, “lacking command over oneself”) is the state of acting against one’s better judgment, not doing what one genuinely wants to do. It encompasses procrastination, lack of self-control, lack of follow-through, and any kind of addictive behavior.
There is deep theory on akrasia; e.g. Guzey (2018)
Much economic research is concerned with the question of why our commitments to ourselves fail, whether it’s lack of self-confidence, lack of willpower in the face of temptations, conflict between the “selves”, or one of many other explanations. We introduce and formalize a new model of commitment failure. We posit that the subjective experience of failing a commitment is frequently indistinguishable from the subjective experience of following it. Thus, we model a person consisting of two selves: Planner (she) and Doer (he). Planner devises the rule for the person’s long-term benefit and Doer follows his perception of Planner’s rule. We analyze the conditions under which Planner is (not) able to devise an effective rule. We show that under some conditions, Doer, while believing that he continues to follow the Planner’s rule, descends into complete procrastination, while, under some conditions, Doer always works to the person’s long-term benefit.
Have a slada of other notes and questions on the theme of akrasia.
1 Role playing time management
Experiment: Pretend to be someone else, a counsellor or something, who would advise you on what to do and really wants the best for you. If you take their imaginary advice on what to do right now, does it make you get more stuff done? It does for me. Why?
2 Discounting
Peter Clark calls this the “Intrapersonal Collective Action Problem,” which I like because it emphasizes that our preferences might be inconsistent across timescales, or even inside ourselves. A complementary concept: “precrastination”.
Tim Harford on hyperbolic discounting:
…what to do about the hyperbolic discounting problem? I have two suggestions. The first helps bring a long-term perspective to the daily to-do list. Don’t draw up your list of tasks first thing in the morning — do it the previous evening, when you will have a slightly more distant perspective. When you do so, think about the two or three tasks you would feel most satisfied to have ticked off. Put those at the top of the list and make them your priority.
The second suggestion flips the telescope around and brings today’s perspective to tomorrow’s commitments. When being invited to do things months in advance, the diary usually looks pretty clear and it’s tempting to say “yes.” But whenever a new invitation arrives, ask yourself not, “should I accept the invitation in March?” but, “would I accept the invitation if it was for this week?”
Aside: I should look up why they always call this “hyperbolic discounting.” Sure, maybe it’s not exponential discounting, but has anyone empirically fit a good hyperbolic curve in particular to typical discounting behaviour, or do we use this term solely because it’s the most clever-sounding thing that’s got fewer syllables than “non-exponential”?
And when we say hyperbolic discounting, are we emphasizing the far future tail, or the immediate inflation? Surely this is a non-parametric estimation problem?
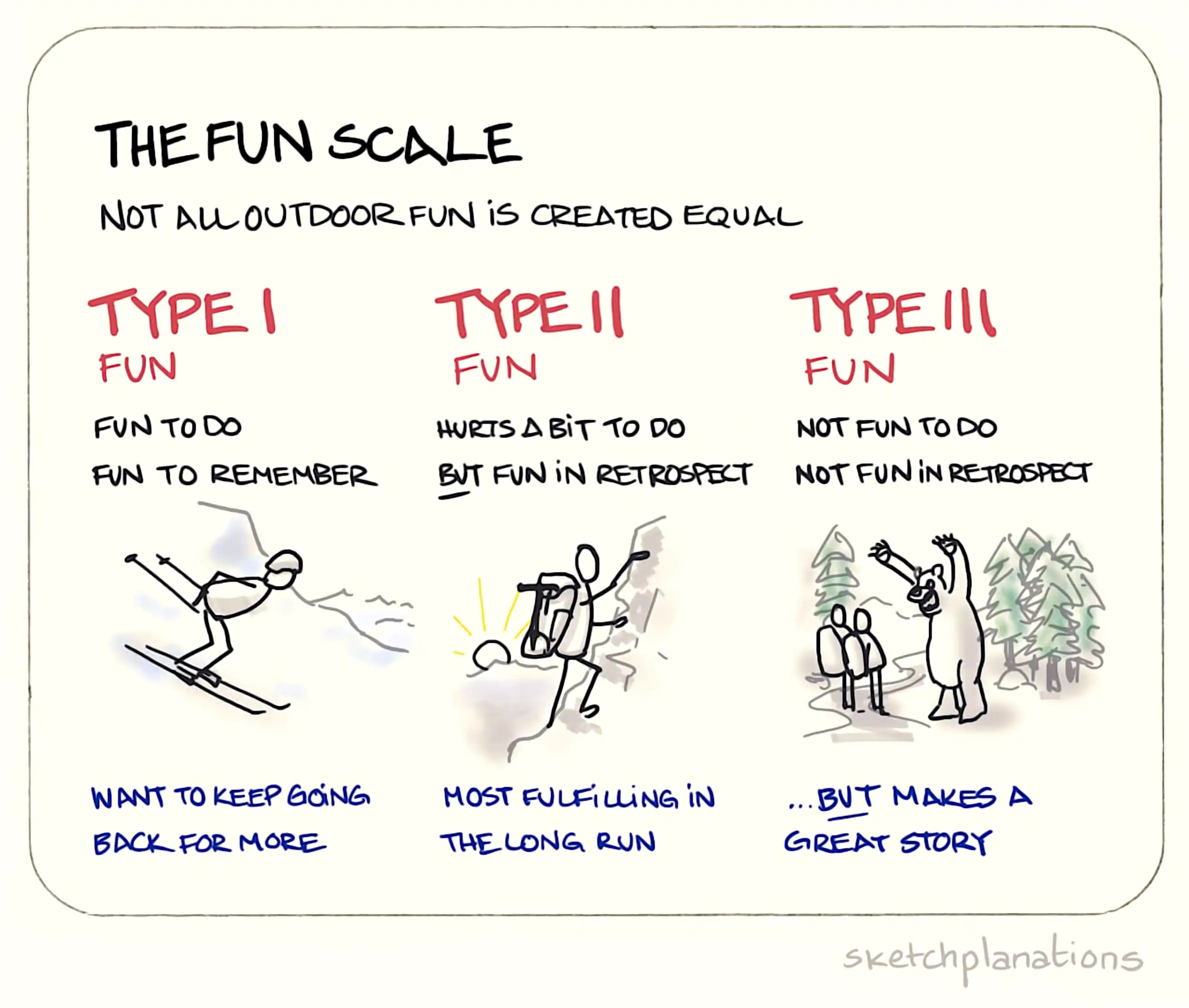
Related: the problem of optimal hedonism.
3 Tying yourself to the mast
Economics is the branch of applied mathematics concerned with the theory and application of constrained maximization. Without exception, every microeconomic decision problem can be framed as the choice of decision variables in order to maximize some objective function (utility, profit, etc.) subject to constraints on the quantity and quality of resources and the manner they are used. To the extent that macroeconomics has theoretical content, it is similarly formulated.
Mathematics is a language. Language strongly influences thought. The language of constrained maximization has led economists to think of constraints as self-evidently welfare-impairing, and to quantify the welfare cost of constraints through use of shadow prices.
Consider, however, the following types of behaviour: My teenage son’s bicycle, though perfectly usable, is to him unaesthetic, because the left pedal is different from the right one; our efforts to remove and replace the odd pedal have defied every tool, technique and muscle. For the past three weeks, he has voluntarily denied himself the convenience and pleasure of using the bicycle, because “if I use it, you and I will never feel the need to take the time to get it down to the bike shop.”
—Maital (1986).
Related: avoiding ease traps.
There’s A Time For Everyone, Scott Alexander argues thusly:
Marriage is a contract, no different in theory than an airline’s contract with an airplane manufacturer. The airline says they’ll buy X planes over the next ten years; the manufacturer says they’ll provide them at such-and-such a price. At the moment of signing, both parties think it’s a good idea. If they both knew it would stay a good idea, a contract would be unnecessary. But something might change. The air travel market might crash, and then the airline would regret having ordered more planes, and want to back out. The price of raw materials might go up, and then the manufacturer would regret offering such a low price, and want to back out themselves. But it would be unfair for the airline to make the airline manufacturer commit to a complicated course of action — building new factories, hiring lots of workers — and then change their mind, leaving them in a worse position than when they started. And it would be unfair for the manufacturer to make the airline commit to a complicated course of action — opening new routes, signing contracts with more airports — and then pull the rug out from under them and demand a higher price. So if you’re committing to a mutual enterprise where both sides are going to make big irreversible changes to satisfy the other, you want a contract where they both agree not to back out, and agree to suffer heavy social and financial sanctions if they do.
(Eliezer Yudkowsky sometimes describes this as ‘changing yourself into a more coherent person in order to become a better bargaining partner,’ which I find strangely romantic.)
4 In practice
See time management.
5 Addiction
See addiction.
6 As an alignment problem
How do I align myself now with all my future and past selves?
7 Incoming
- Alexey Guzey, Every productivity thought I’ve ever had, as concisely as possible
- Coherent Extrapolated Volition
- Extrapolated volition (normative moral theory)
- Jan_Kulveit, rosehadshar, The self-unalignment problem phrases this as an alignment problem, which feels right to me.